The Lagoon Nebula
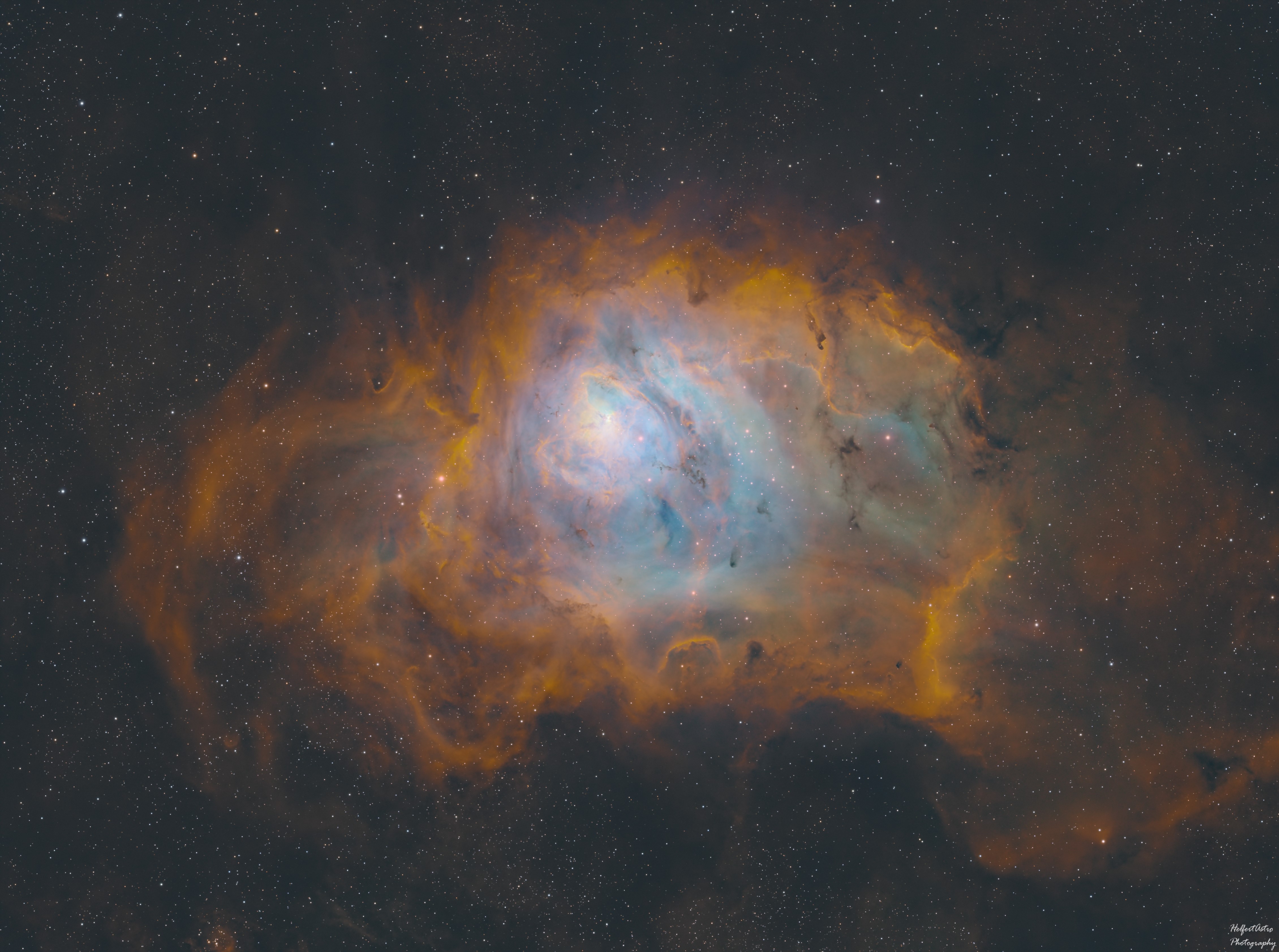

Acquisition: AT115EDT. July, 2024.
The Lagoon and Trifid Nebula

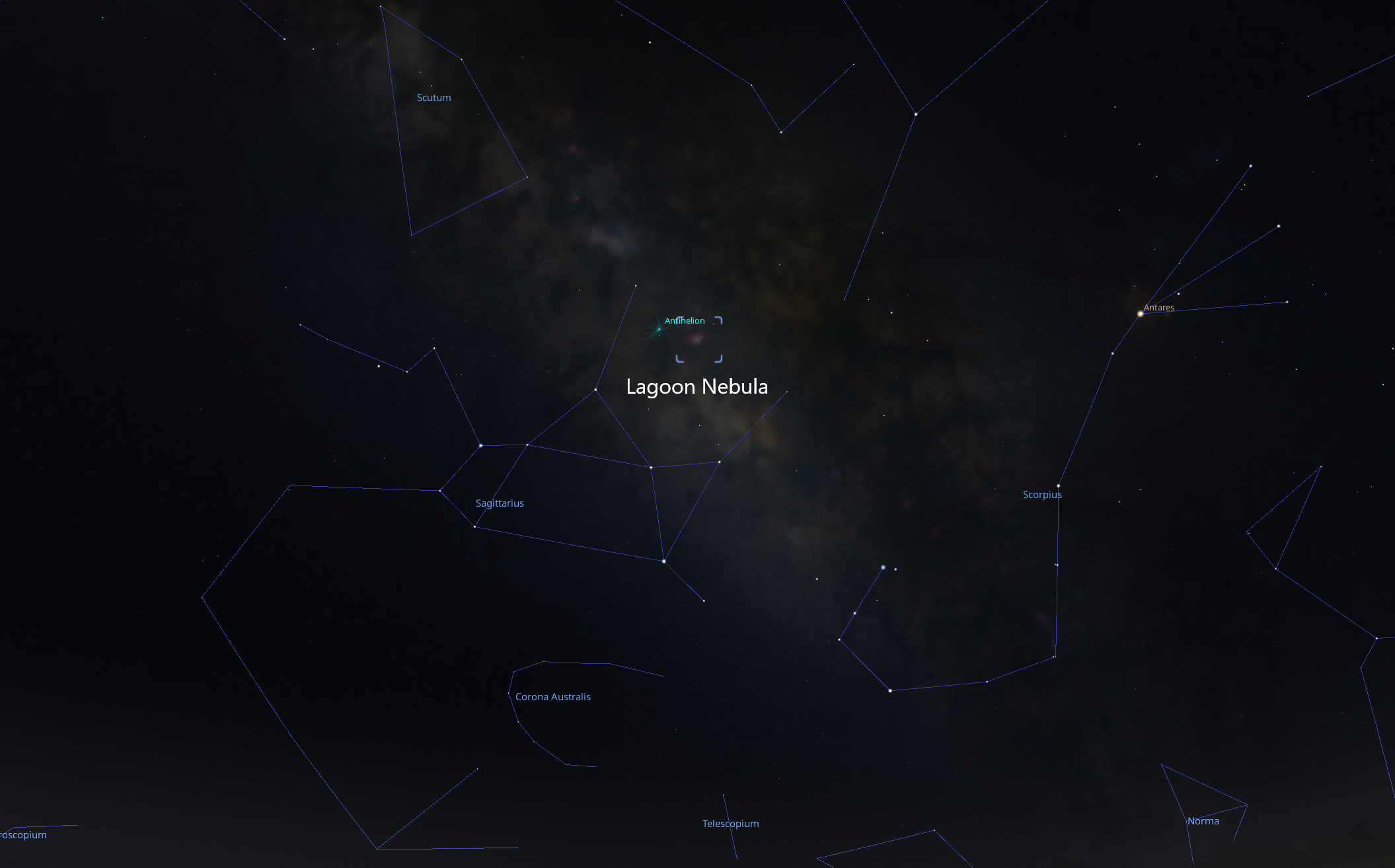
Location in Sky
Acquisition: Redcat 51. August, 2022
Quick Facts
Description
The Lagoon (M8) and Trifid (M20) Nebula are located at the spout of the "teapot" in the Sagittarius constellation. Sagittarius is located in the densest part of the Milky Way core.The brighter ball on the left is the Trifid Nebula, which is a larger, but further nebula. The area the Lagoon nebula covers is 55 x 110 Lightyears, but does not appear this way to us since it is roughly 5,200 Lightyears from the Earth. With a magnitude of 6, this is the darkest a deep-sky object can be viewable with the naked eye, given you have exceptional eyesight. Looking at the night sky, the Lagoon nebula would be as large as two full moons. Both nebulas are comprised of mostly ionized Hydrogen gas. When the energy from new or dying stars passes through these giant clouds of Hydrogen, it ionizes the gas which makes it glow. When the energy is low, it will glow with a red tint. The darker parts of these nebula are where most of their stars are being formed.