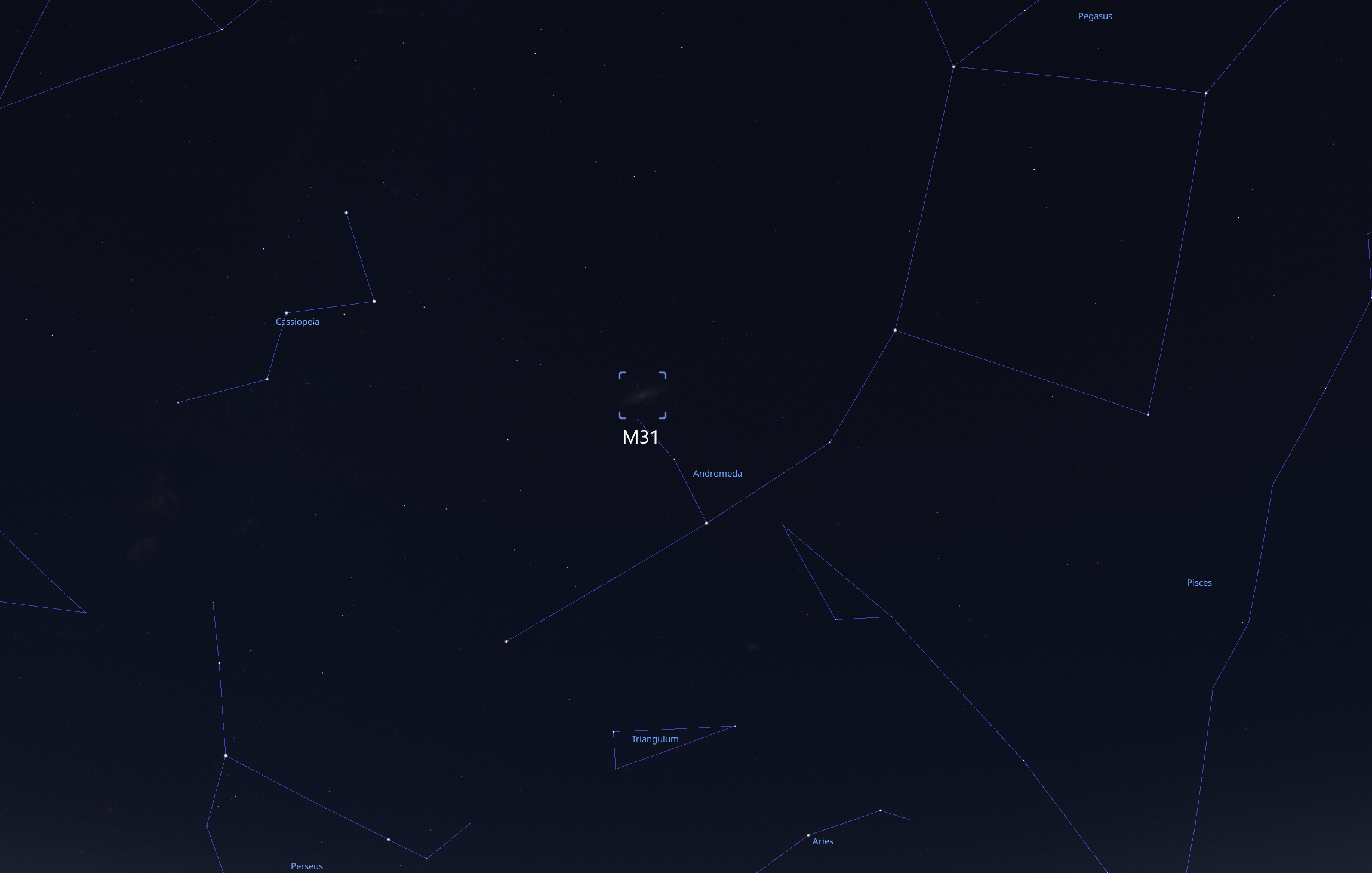
Andromeda

Location in Sky
Acquisition: SkyWatcher 130-PDS. November, 2022
Quick Facts
Description
Andromeda, or M31 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the Andromeda constellation about 2.5 million light-years from earth. Discovered around the year 964 by Abd Al-Rahman Al Sufi. Abd recorded Andromeda in his book, “Book of Fixed Stars” as a “nebulous smear” or a “small cloud”. At this time, it was believed that everything was contained within the Milky Way. In the year 1885, a supernova named Nova 1885, was seen in Andromeda, and has been the only one seen in Andromeda since then. It was only in 1920 did Edwin Hubble prove that this was in fact a galaxy, and that there are billions more just like it. So far, we have determined there are more than 1 trillion stars in the Andromeda galaxy, which beats out the Milky Way by roughly 200 billion, though as our abilities to detect matter more accurately improve over the years, this will change. Andromeda has two distinct satellite galaxies which can be seen directly above and below the galaxy known as M32 (above) and M110 (below). A study was done in 2006 by a team on scientists that determined the Andromeda galaxy was most likely formed 10 billion years ago by collisions of smaller protogalaxies. It is certain that in around 4.5 billion years, Andromeda and the Milky Way will collide. Since galaxies are mostly empty space, it is believed that our solar system won’t be affected and that no stars will collide. This collision will sling galactic matter outside of the galaxies, and will take a few billion years to fully combine. Andromeda and the Milky Way are located in what is called the “Local group”, which is a group of over 30 galaxies within the diameter of roughly 10 million light-years. M31 and the Milky Way are the two largest, with M33 (Triangulum Galaxy) coming in third. With an apparent magnitude of 3.44, M31 is just bright enough to be seen with the unaided eye.